Section 1: Objective
1. This regulation shall set out the general safety requirements in ensuring protection of people and the environment against the harmful effects of ionizing radiation and for the safety of radiation sources.
2. This regulation shall harmonize the requirements applicable in the Kingdom with the international best practices in order to achieve the highest standards of safety in activities and facilities that give rise to radiation risks.
Section 2: Scope
3. This regulation applies to all activities and facilities including practices, that are carried out in the Kingdom which involve, or could involve, risk from exposure to ionizing radiation in planned, emergency and existing situations.
4. This regulation shall be applicable to occupational, public and medical exposure in the Kingdom.
5. The safety requirements set forth in this regulation shall apply to any person involved in activities and facilities including practices defined under the Law as specified in this regulation.
6. Other safety requirements, complementary to this regulation shall apply for certain activities and facilities, such as for nuclear installations.
7. This regulation is complemented by specific requierment for radiation protection and safety as specified by NRRC.
Section 3: Exclusions
8. The following exposures are excluded from the scope of this regulation:
- Exposures from natural radioactivity in the body;
- Cosmic radiation at the surface of the earth;
- Any other radiation sources that are essentially unamenable to control as may be determined by the NRRC.
Section 4: Definitions

Accident
Any unintended event, including operating errors, equipment failures and other mishaps, the consequences or potential consequences of which are not negligible from the point of view of protection and safety.
Activation
The process of inducing radioactivity in the matter by irradiation of that matter.
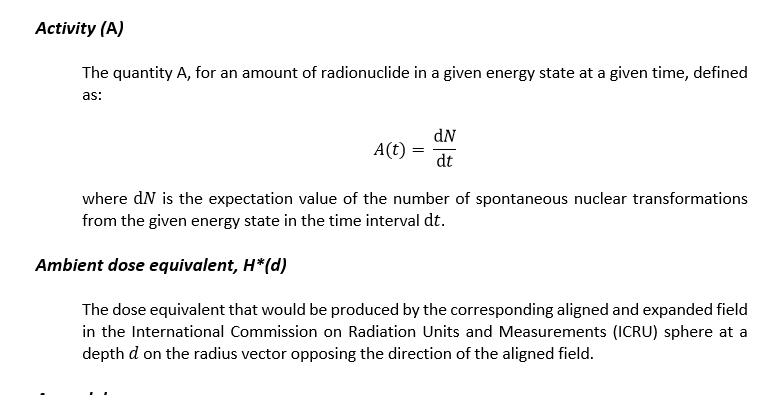
Activity
The production, use, possession, storage, transport, import, or export of radioactive, nuclear or nuclear-related items; the siting, construction, commissioning, operation or decommissioning of facilities; radioactive waste management and site rehabilitation; or any other act specified by the Commission in accordance with its laws.
Annual dose
The dose from external exposure in a year plus the committed dose from intakes of radionuclides in that year.
Applicant
Any person applying to the NRRC for authorization to undertake specified activities and facilities including practices. Strictly, an applicant would be such from the time at which an application is submitted until the requested authorization is either granted or refused.
Area monitoring
A form of workplace monitoring in which an area is monitored by taking measurements at different points in that area.
Assessment
The process, and the result, of analyzing systematically and evaluating the hazards associated with sources and practices, and associated protection and safety measures.
Authorization
The granting by the NRRC of written permission for a person to conduct specified activities.
Authorized limit
A limit on a measurable quantity, established or formally accepted by the NRRC.
Authorized person
Person granted authorization under this regulation and/or the relevant Commission Laws.
Carers and comforters
Persons who willingly and voluntarily help (other than in their occupation) in the care, support and comfort of patients undergoing radiological procedures for medical diagnosis or medical treatment.
Clearance
The removal of radioactive material or radiation source subject to the Law from the control imposed thereon by the NRRC because the radiation exposure resulting therefrom is too small to warrant the application of such control.
Clearance level
A value, established by the NRRC and expressed in terms of activity (A) concentration, at or below which regulatory control may be removed from a source of radiation within a notified or authorized practice.
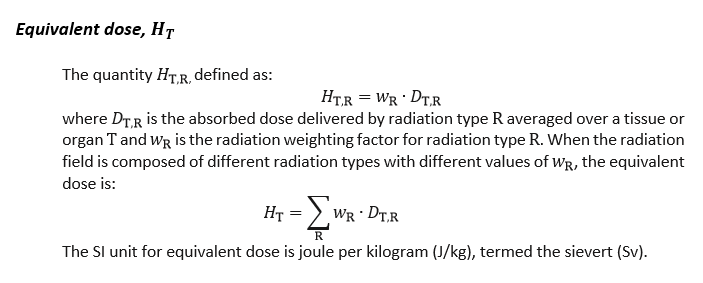
Committed dose
The lifetime dose expected to result from an intake.
Committed effective dose, E(τ)
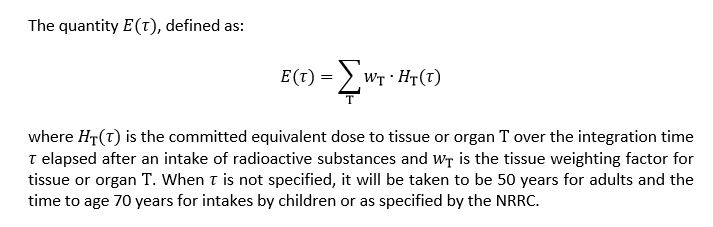
Confinement
Prevention or control of releases of radioactive material to the environment in operation or in accidents.
Constraint
A prospective and source related value of individual dose (dose constraint) or of individual risk (risk constraint) that is used in planned exposure situations as a parameter for the optimization of protection and safety for the source, and that serves as a boundary in defining the range of options in optimization.
Consumer product
A device or manufactured item into which radionuclides have deliberately been incorporated or produced by activation, or which generates ionizing radiation, and which can be sold or made available to members of the public without special surveillance or regulatory control after sale or any product as determined by NRRC.
Containment
Methods or physical structures designed to prevent or control the release and the dispersion of radioactive substances.
Contamination
Radioactive substances on surfaces, or within solids, liquids or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirable, or the process giving rise to their presence in such places.
Control
The function or power or (usually as controls) means of directing, regulating or restraining.
Controlled area
A defined area in which specific protection measures and safety provisions are or could be required for controlling exposures or preventing the spread of contamination in normal working conditions, and preventing or limiting the extent of potential exposures.
Decontamination
The complete or partial removal of contamination by a deliberate physical, chemical or biological process.
Deterministic effect
A radiation induced health effect for which generally a threshold level of dose exists above which the severity of the effect is more significant for a higher dose.
Diagnostic reference level
A level used in medical imaging to indicate whether in routine conditions, the dose to the patient or the amount of radiopharmaceuticals administered in a specified radiological procedure for medical imaging is unusually high or unusually low for that procedure.

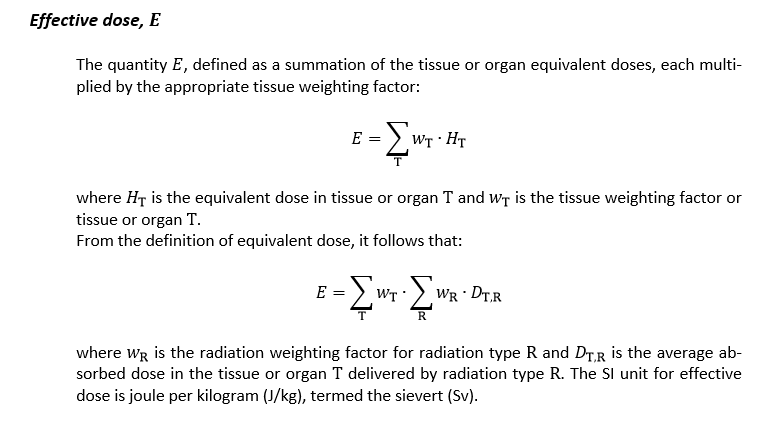
Dose
- A measure of the energy deposited by radiation in a target.
- Absorbed dose, committed equivalent dose, committed effective dose, effective dose, equivalent dose or organ dose, as indicated by the context.
Dose assessment
Assessment of the dose(s) to an individual or group of people.
Dose constraint
A prospective and radiation source related value of individual dose that is used in planned exposure situations as a parameter for the optimization of protection and safety for the source, and that serves as a boundary in defining the range of options in optimization.
Dose limit
The value of a quantity used in certain specified activities or circumstances that must not be exceeded.
Emergency
A non-routine situation that necessitates prompt action, primarily to mitigate a hazard or adverse consequences for human health and safety, quality of life, property or the environment. This includes nuclear or radiological emergencies and conventional emergencies such as fires, release of hazardous chemicals, storms or earthquakes. It includes situations for which prompt action is warranted to mitigate the effects of a perceived hazard.
Emergency exposure situation
A situation of exposure that arises as a result of an accident, a malicious act or other unexpected events, and requires prompt action in order to avoid or reduce adverse consequences.
Emergency plan
A description of the objectives, policy and concept of operations for the response to an emergency and of the structure, authorities and responsibilities for a systematic, coordinated and effective response. The emergency plan serves as the basis for the development of other plans, procedures and checklists.
Emergency preparedness
The capability to take actions that will effectively mitigate the consequences of an emergency for human health and safety, quality of life, property and the environment.
Emergency procedures
A set of instructions describing in detail the actions to be taken by the response personnel in an emergency.
Emergency response
The performance of actions to mitigate the consequences of an emergency for human health and safety, quality of life, property and the environment. It may also provide a basis for the resumption of normal social and economic activity.
Emergency worker
A person having specified duties as a worker in response to an emergency.
Employer
A person with recognized responsibilities, commitments and duties towards a worker in the employment of the person by virtue of a mutually agreed relationship.
Environment
The conditions under which people, animals and plants live or develop and which sustain all life and development; especially such conditions as affected by human activities.
Environmental monitoring
The measurement of external dose rates due to sources in the environment or of radionuclide concentrations in environmental media.
Exemption
The NRRC's decision that a radiation source or certain radiation practice need not be subject to its partial or full control on the basis that the exposure to radiation resulting from such source or practice is too low to warrant application of such control, or that this is the optimum option available after taking necessary preventive measures for minimizing the risks of exposure to ionizing radiation.
Event
In the context of the reporting and analysis of events, an event is any occurrence unintended by the worker, including operating error, equipment failure or another mishap, and deliberate action on the part of others, the consequences or potential consequences of which are not negligible from the point of view of protection and safety.
Exemption level
A value, established by the NRRC and expressed in terms of activity (A) concentration, total activity (A), dose rate or radiation energy, at or below which a source of radiation need not be subject to some or all aspects of regulatory control.
Existing exposure situation
A situation of exposure that already exists when a decision on the need for control needs to be taken.
Exposure
The state or condition of being subject to irradiation.
Exposure pathway
A route by which radiation or radionuclides can reach humans and cause exposure.
Facility
This shall include a nuclear facility; installation where a radiation source is used; mining and raw materials processing facilities, such as uranium mines; radioactive waste management facilities; and any other locations where radioactive materials are produced, processed, used, handled, stored or disposed of to the extent warranted by safety and security.
Graded approach
For a system of control a process or method in which the stringency of the control measures and conditions to be applied is commensurate, to the extent practicable, with the likelihood and possible consequences of, and the level of risk associated with, a loss of control.
Health professional
An individual who has been formally recognized through appropriate national procedures to practice a profession related to health (e.g. medicine, dentistry, chiropractic, podiatry, nursing, medical physics, medical radiation technology, radiopharmacy, occupational health).
Health screening program
A program in which health tests or medical examinations are performed for the purpose of early detection of disease.
Human factors
Engineering in which factors that could influence human performance and that could affect safety are understood and are taken into account, especially in the design and operation of facilities.
Individual monitoring
Monitoring using measurements by equipment worn by individuals, or measurements of quantities of radioactive substances in or on, or taken into, the bodies of individuals, or measurements of quantities of radioactive substances excreted from the body by individuals.
Inspection imaging device
An imaging device designed specifically for imaging persons or cargo conveyances to detect concealed objects on or within the human body or within cargo or a vehicle.
Intake
- The act or process of taking radionuclides into the body by inhalation or ingestion or through the skin.
- The activity (A) of a radionuclide taken into the body in a given period or as a result of a given event.
Investigation level
The value of a quantity such as effective dose, intake or contamination per unit area or volume at or above which an investigation would be conducted.
Justification
1. Justification for a planned exposure situation
The process of determining for a planned exposure situation whether a practice is, overall, beneficial, i.e. whether the expected benefits to individuals and to society from introducing or continuing the practice outweigh the harm (including radiation detriment) resulting from the practice.
2. Justification for a existing or emergency situation
The process of determining for an emergency exposure situation or an existing exposure situation whether a proposed protective action or remedial action is likely, overall, to be beneficial; i.e., whether the expected benefits to individuals and to society (including the reduction in radiation detriment) from introducing or continuing the protective action or remedial action outweigh the cost of such action and any harm or damage caused by the action.
Limit
The value of a quantity used in certain specified activities or circumstances that must not be exceeded.
Management system
A set of interrelated or interacting elements (system) for establishing policies and objectives and enabling the objectives to be achieved in an efficient and an effective manner.
Medical exposure
Exposure incurred by patients for the purposes of medical or dental diagnosis or treatment; by carers and comforters; and by volunteers subject to exposure as part of a program of biomedical research.
Medical physicist
A Health professional recognized by the competent authority of the Kingdom.
Medical radiation facility
A medical facility in which radiological procedures are performed.
Medical radiation technologist
A health professional, with specialist education and training in medical radiation technology, competent to perform radiological procedures, on delegation from the radiological medical practitioner, in one or more of the specialties of medical radiation technology.
Medical radiological equipment
Radiological equipment used in medical radiation facilities to perform radiological procedures that either delivers an exposure of an individual or directly controls or influences the extent of such exposure. The term applies to radiation generators, such as machines or medical linear accelerators; to devices containing sealed sources, such as 60Co teletherapy units; to devices used in medical imaging to capture images, such as gamma cameras, image intensifiers or flat panel detectors, and to hybrid systems such as positron emission tomography-computed tomography scanners.
Member of the public
For purposes of protection and safety, in a general sense, any individual in the population except when subject to occupational exposure or medical exposure. For the purpose of verifying compliance with the annual dose limit for public exposure, this is the representative person.
Monitoring
The measurement of dose, dose rate or activity (A) for reasons relating to the assessment or control of exposure to radiation or exposure due to radioactive substances, and the interpretation of the results.
Natural background
The doses, dose rates or activity (A) concentrations associated with natural sources, or any other sources in the environment that are not amenable to control.
Natural source
A naturally occurring source of radiation, such as the sun and stars (sources of cosmic radiation) and rocks and soil (terrestrial sources of radiation), or any other material whose radioactivity is for all intents and purposes due only to radionuclides of natural origin, such as products or residues from the processing of minerals; but excluding radioactive material for use in a nuclear installation and radioactive waste generated in a nuclear installation.
Notification
A document submitted to the NRRC by a person intending to carry out any activity or practice or to establish a radiation facility involving radiation sources.
Nuclear fuel cycle
All operations associated with the production of nuclear energy. These include:
- Mining and processing of uranium ores or thorium ores;
- Enrichment of uranium;
- Manufacture of nuclear fuel;
- Operation of nuclear reactors (including research reactors);
- Reprocessing of spent fuel;
- All waste management activities (including decommissioning) relating to operations associated with the production of nuclear energy;
- Any related research and development activities.
Nuclear installation
Any nuclear facility subject to authorization that is part of the nuclear fuel cycle, except facilities for the mining or processing of uranium ores or thorium ores and radioactive waste disposal facilities.
Nuclear or radiological emergency
Any emergency, which results or is likely to result in exposure risk to ionizing radiation
Occupational exposure
Exposure of workers incurred in the course of their work.
Operational limits and conditions
A set of rules setting forth parameter limits, the functional capability and the performance levels of equipment and personnel approved by the NRRC for safe operation of an authorized facility.
Optimization of protection and safety
The process of determining what level of protection and safety would result in the magnitude of individual doses, the number of individuals (workers and members of the public) subject to exposure and the likelihood of exposure being “as low as reasonably achievable, economic and social factors being taken into account" (ALARA). For medical exposures of patients, the optimization of protection and safety is the management of the radiation dose to the patient commensurate with the medical purpose.
Planned exposure situation
The situation of exposure that arises from the planned operation of a source or from a planned activity that results in an exposure due to a source.
Planning target volume
A geometrical concept used in radiation therapy for planning medical treatment with consideration of the net effect of movements of the patient and of the tissues to be irradiated, variations in size and shape of the tissues, and variations in beam geometry such as beam size and beam direction.
Potential exposure
Prospectively considered exposure that is not expected to be delivered with certainty but that may result from an anticipated operational occurrence or accident at a source or owing to an event or sequence of events of a probabilistic nature, including equipment failures and operating errors.
Practice
Any human activity that causes or is likely to cause exposure to ionizing radiation, excluding procedures of medical diagnosis or treatment of patients by healthcare practitioners.
Projected dose
The dose that would be expected to be received if planned protective actions were not taken.
Protection (against radiation)
See Radiation Protection.
Protection and safety
The protection of people against exposure to ionizing radiation or exposure due to radioactive material and the safety of sources, including the means for achieving this, and the means for preventing accidents and for mitigating the consequences of accidents if they do occur.
Protective action
An action for the purposes of avoiding or reducing doses that might otherwise be received in an emergency exposure situation or an existing exposure situation.
Providers of consumer products
Designers, manufacturers, producers, constructors, installers, distributors, sellers, and importers and exporters of consumer products.
Public exposure
Exposure incurred by members of the public due to sources in planned exposure situations, emergency exposure situations and existing exposure situations, excluding any occupational exposure or medical exposure.
Qualified expert
An individual who is duly recognized as having expertise in a relevant field of specialization, e.g. medical physics, radiation protection, occupational health, fire safety, quality management or any relevant engineering or safety specialty.
Quality assurance
The function of a management system that provides confidence that specified requirements will be fulfilled.
Radiation
The ionizing radiation as defined in the Law.
Radiation detriment
The total harm that would eventually be incurred by a group that is subject to exposure and by its descendants as a result of the group's exposure to radiation from a source.
Radiation generator
A device capable of generating ionizing radiation, such as ![]() , neutrons, electrons or other charged particles, that may be used for scientific, industrial or medical purposes.
, neutrons, electrons or other charged particles, that may be used for scientific, industrial or medical purposes.
Radiation protection
The protection of people from the harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation and the means for achieving this.
Radiation source
Any radiation generator, radioactive source, or any other radioactive material outside the nuclear fuel cycles of research and power reactors.
Radiation safety officer (RSO)
A competent person certified by the NRRC in radiation safety matters relevant for a given type of practice who is designated by the authorized person or employer to oversee the application of regulatory requirements.
Radiation protection program
Systematic arrangements that are aimed at providing adequate consideration of radiation protection measures.
Radiation risks
Detrimental health effects of exposure to radiation (including the likelihood of such effects occurring), and any other safety related risks (including those to the environment) that might arise as a direct consequence of:
a.Exposure to radiation;
b.The presence of radioactive material (including radioactive waste) or its release to the environment;
c.A loss of control over a nuclear reactor core, nuclear chain reaction, radioactive source or any other source of radiation.

*INTERNATIONAL COMMISSION ON RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION, The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, Publication 103, Elsevier (2007).
Radioactive material
Any material from which ionizing radiation is emitted, whether spontaneously or within other equipment, and which is designated as subject to the control of the NRRC, including naturally occurring radioactive materials.
Radioactive Source
Any radioactive material permanently sealed in a capsule or closely bonded and in a solid form.
Radioactive substance
Any substance that contains radioactivity, and gives no indication of the magnitude of the hazard involved that may be designated by the NRRC as being subject to regulatory control.
Radioactive waste
Any material, regardless of its physical form, resulting from activities, practices or interventions such as decontamination, for which no further use is foreseen and which contains or is contaminated with radioactive substances, and has radiological activity (A) or concentration higher than the level set for clearance from regulatory control.
Radioactive waste management
All administrative and operational activities involved in the handling, pretreatment, treatment, conditioning, transport, storage and disposal of radioactive waste.
Radiological medical practitioner
A health professional with Specialist in education and training in the medical uses of radiation, who is competent to perform independently or to oversee radiological procedures in a given specialty.
Radiological procedure
A medical imaging procedure or therapeutic procedure that involves ionizing radiation, such as a procedure in diagnostic radiology, nuclear medicine or radiation therapy, or a planning procedure, image guided interventional procedure or other interventional procedure involving radiation delivered by a radiation generator, a device containing a sealed source or an unsealed source, or by means of a radiopharmaceutical administered to a patient.
Radionuclides of natural origin
Radionuclides that occur naturally on Earth in significant quantities.
Radiopharmacis
t
A health professional, with Specialist in Education and training in radiopharmacy, who is competent to prepare and dispense radiopharmaceuticals used for the purposes of medical diagnosis and radionuclide therapy.
Reference level
For an emergency exposure situation or an existing exposure situation, the level of risk or activity (A) concentration above which it is not appropriate to plan to allow exposures to occur and below which optimization of protection and safety would continue to be implemented.
Referring medical practitioner
A health professional who, in accordance with national requirements, may refer individuals to a radiological medical practitioner for medical exposure.
Regulatory control
Any form of control or regulation applied to activities and facilities including practices by the NRRC for reasons relating to nuclear safety and radiation protection or nuclear security or safeguards.
Relative biological effectiveness (RBE)
A relative measure of the effectiveness of different radiation types at inducing a specified health effect expressed as the inverse ratio of the absorbed doses of two different radiation types that would produce the same degree of a defined biological endpoint.
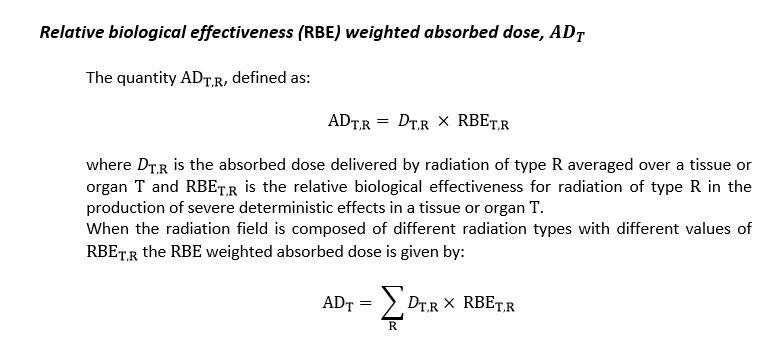
Remedial action
The removal of a source or the reduction of its magnitude (in terms of activity (A) or amount) for the purposes of preventing or reducing exposures that might otherwise occur in an existing exposure situation.
Remediation
Any measures that may be carried out to reduce the radiation exposure due to existing contamination of land areas through actions applied to the contamination itself (the source) or to the exposure pathways to humans.
Representative person
An individual receiving a dose that is representative of the doses to the more highly exposed individuals in the population.
Response organization
An organization designated or otherwise recognized by the Kingdom as being responsible for managing or implementing any aspect of an emergency response.
Risk
A multiattribute quantity expressing hazard, danger or chance of harmful or injurious consequences associated with exposures or potential exposure. It relates to quantities such as the probability that specific deleterious consequences may arise and the magnitude and character of such consequences.
Safety assessment
Assessment of all aspects of an activity that are relevant to protection and safety; for an authorized facility. This includes siting, design and operation of the facility.
Safety culture
The assembly of characteristics and attitudes in organizations and individuals which establishes that, as an overriding priority, protection and safety issues receive the attention warranted by their significance.
Safety measure
Any action that might be taken, a condition that might be applied or procedure that might be followed to fulfill the requirements of Safety Requirements.
Scenario
A postulated or assumed set of conditions and/or events.
Security
Prevention and detection of any theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer (or any other criminal act) involving nuclear, nuclear-related or radioactive materials and associated facilities.
Source
Anything that may cause radiation exposure such as by emitting ionizing radiation or by releasing radioactive substances or radioactive material and can be treated as a single entity for purposes of protection and safety.
Sealed source
Radioactive source in which the radioactive material is permanently sealed in a capsule or closely bonded and in a solid form.
Source monitoring
The measurement of activity (A) in radioactive material being released to the environment or of external dose rates due to sources within an activity or a facility.
Standards dosimetry laboratory
A laboratory, designated by the NRRC that possesses the recognition necessary for the purpose of developing, maintaining or improving primary or secondary standards for radiation dosimetry.
Storage
The holding of radioactive sources, radioactive material, spent fuel or radioactive waste in a facility that provides for their/its containment, with the intention of retrieval.
Structures, systems and components
A general term encompassing all of the elements (items) of an activity or a facility that contribute to protection and safety, except human factors.
Supervised area
A defined area not designated as a controlled area but for which occupational exposure conditions are kept under review, even though specific protection measures or safety provisions are not normally needed.
Supplier (of a source)
Any person to whom the authorized person assigns duties, totally or partially, in relation to the design, manufacture, production or construction of a source.
Technical Services Organizations
An organization that provide expertise and services to support nuclear and radiation safety and all related scientific and technical issue.
Tissue weighting factor, ![]()
The multiplier of the equivalent dose to a tissue or organ used for purposes of radiation protection to account for the different sensitivities of different tissues or organs to the induction of stochastic effects of radiation.
Transport
All operations and conditions associated with the movement of nuclear and radioactive material, whether through, from or into the territory of the Kingdom.
Unsealed source
A radioactive source in which the radioactive material is neither (a) permanently sealed in a capsule nor (b) closely bonded and in a solid form.
Worker
Any person who works, whether full time, part-time or temporarily, for an employer and who has recognized rights and duties in relation to occupational radiation protection.
Workers' health surveillance
Medical supervision intended to ensure the initial and continuing fitness of workers for their intended tasks.
Workplace monitoring
Monitoring using measurements made in the working environment.